Universe Expanding More Rapidly Than Previously Thought – New Research
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – A group of astronomers led by the University of California, Davis has obtained new data that suggest the universe is expanding more rapidly than previously thought.
Using Keck Observatory’s AO system with the Near-Infrared Camera, second generation (NIRC2) instrument on the Keck II telescope, Chen and his team obtained local measurements of three well-known lensed quasar systems: PG1115+ 080, HE0435-1223, and RXJ1131-1231.
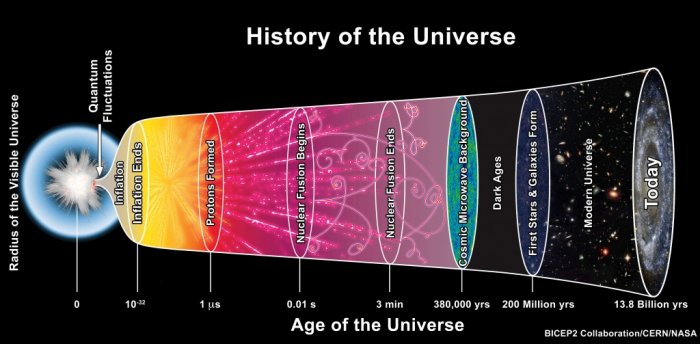 An artist’s depiction of the standard model of cosmology. Credit: BICEP2 Collaboration/CERN/NASA
An artist’s depiction of the standard model of cosmology. Credit: BICEP2 Collaboration/CERN/NASA
The team’s new measurement of the Hubble Constant, or the expansion rate of the universe, involved a different method. They used NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in combination with W. M. Keck Observatory’s Adaptive Optics (AO) system to observe three gravitationally-lensed systems. This is the first time ground-based AO technology has been used to obtain the Hubble Constant.
“When I first started working on this problem more than 20 years ago, the available instrumentation limited the amount of useful data that you could get out of the observations,” co-author Chris Fassnacht, Professor of Physics at UC Davis, said in a press release.
“In this project, we are using Keck Observatory’s AO for the first time in the full analysis. I have felt for many years that AO observations could contribute a lot to this effort.”
To rule out any bias, the team conducted a blind analysis; during the processing, they kept the final answer hidden from even themselves until they were convinced that they had addressed as many possible sources of error as they could think of. This prevented them from making any adjustments to get to the “correct” value, avoiding confirmation bias.
“When we thought that we had taken care of all possible problems with the analysis, we unblind the answer with the rule that we have to publish whatever value that we find, even if it’s crazy. It’s always a tense and exciting moment,” says lead author Geoff Chen, a graduate student at the UC Davis Physics Department.
The unblinding revealed a value that is consistent with Hubble Constant measurements taken from observations of “local” objects close to Earth, such as nearby Type Ia supernovae or gravitationally-lensed systems; Chen’s team used the latter objects in their blind analysis.
The team’s results add to growing evidence that there is a problem with the standard model of cosmology, which shows the universe was expanding very fast early in its history, then the expansion slowed down due to the gravitational pull of dark matter, and now the expansion is speeding up again due to dark energy, a mysterious force.
Read more – here.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff
Related Posts
-
 Surprising Activity Of Supermassive Black Hole At The Center Of Milky Way
No Comments | Sep 13, 2019
Surprising Activity Of Supermassive Black Hole At The Center Of Milky Way
No Comments | Sep 13, 2019 -
 Ancient Astronomical Observations Shed New Light On Solar Storms, Auroras And Other Celestial Phenomena
No Comments | Apr 11, 2017
Ancient Astronomical Observations Shed New Light On Solar Storms, Auroras And Other Celestial Phenomena
No Comments | Apr 11, 2017 -
 Star Spaghettified By Black Hole Observed By Astronomers For The First Time
No Comments | May 12, 2021
Star Spaghettified By Black Hole Observed By Astronomers For The First Time
No Comments | May 12, 2021 -
 Galaxies As “Cosmic Cauldrons” – Observations Of NGC 300 Spiral Galaxy
No Comments | Jun 3, 2019
Galaxies As “Cosmic Cauldrons” – Observations Of NGC 300 Spiral Galaxy
No Comments | Jun 3, 2019 -
 Map Of Local Void Of The Milky Way Created
No Comments | Jul 23, 2019
Map Of Local Void Of The Milky Way Created
No Comments | Jul 23, 2019 -
 Earth’s Periodic Mass Extinctions Linked to Planet X – Researcher Says
No Comments | Mar 31, 2016
Earth’s Periodic Mass Extinctions Linked to Planet X – Researcher Says
No Comments | Mar 31, 2016 -
 Heavy Elements Were Created After The Big Bang
No Comments | Nov 30, 2018
Heavy Elements Were Created After The Big Bang
No Comments | Nov 30, 2018 -
 Sophisticated Algorithm Will Identify Jupiter’s And Saturn’s Twins
No Comments | Jun 27, 2019
Sophisticated Algorithm Will Identify Jupiter’s And Saturn’s Twins
No Comments | Jun 27, 2019 -
 ‘Closest Black Hole’ System Found To Contain No Black Hole
No Comments | Mar 2, 2022
‘Closest Black Hole’ System Found To Contain No Black Hole
No Comments | Mar 2, 2022 -
 Strange Galaxy Dragonfly 44 – Was It Really Anomalous And Unique?
No Comments | Oct 14, 2020
Strange Galaxy Dragonfly 44 – Was It Really Anomalous And Unique?
No Comments | Oct 14, 2020
