Astronomy
First Black Hole Image: A Gravitomagnetic Monopole As An Alternative Explanation
| November 18, 2021
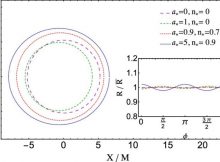
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) has recently mapped the central compact object of the galaxy M87 with an unprecedented angular resolution. Though the
Read More
