Stellar Cradles And Graves Seen In Farthest Galaxy Ever
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – New observations using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have distinguished the sites of star formation and a possible site of star death from the surrounding nebula in a galaxy 13.2 billion light-years away.
This is the farthest that such structures have been observed.
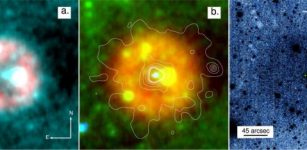
(Left) Dust is shown in red, oxygen is shown in green, and starlight imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope is shown in blue. (Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), Y. Tamura et al., NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope) (Right) ALMA dust emissions shown alone. A vertically elongated elliptical cavity, a possible superbubble, is visible in the central region. (Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), Y. Tamura et al.)
A team led by Yoichi Tamura, an astronomer at Nagoya University, attempted high-resolution observations of MACS0416_Y1, located 13.2 billion light-years away in the constellation Eridanus. Previous observations of this galaxy by the same team had detected radio waves emitted by both oxygen and dust, two components of interstellar nebulae. Detailed observations of the distribution of dust and oxygen can provide clues about how stars are born and die within nebulae, but the observations had lacked the resolution needed to see the structure of the nebulae.
This time the team observed with ALMA for 28 hours, zooming in on MACS0416_Y1. The results showed that the dust signal regions and oxygen emission regions are intricately intertwined, avoiding each other, suggesting the process where newly formed stars within the nebulae ionize the surrounding gas.
Furthermore, the team found a massive cavity spanning approximately 1,000 light-years in the dust dominated regions. When many new, massive and short-lived stars are born together, the resulting successive supernova explosions create enormous “superbubbles” in the nebulae. The discovered cavity may indeed be such a superbubble.
Takuya Hashimoto from the University of Tsukuba describes the observation performance as follows: “It corresponds to capturing the extremely weak light emitted by two fireflies located 3 centimeters apart on the summit of Mount Fuji as seen from Tokyo, and being able to distinguish between those two fireflies.”
Measurements of the motion of the gas in the nebulae indicate an environment where many stars may form together as massive clusters.
“In the future, more detailed information can be obtained by conducting high-resolution observations of these star clusters themselves, using instruments such as the James Webb Space Telescope and the planned Extremely Large Telescopes,” team leader Tamura explains the future prospects based on these results.
These observation results were published as Yoichi Tamura et al. “The 300 pc Resolution Imaging of a z = 8.31 Galaxy: Turbulent Ionized Gas and Potential Stellar Feedback 600 Million Years after the Big Bang” in the Astrophysical Journal.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff