Smith Cloud: Science Facts About Giant Gas Cloud On Collision Course With Milky Way
MessageToEagle.com – The Smith Cloud is a giant hydrogen gas cloud that is on a collision course with the Milky Way Galaxy. It travels extremely fast and the impact will occur in the distant future. What do astronomers know about this monstrous cloud?
In this article we present some facts and information about the Smith Cloud.
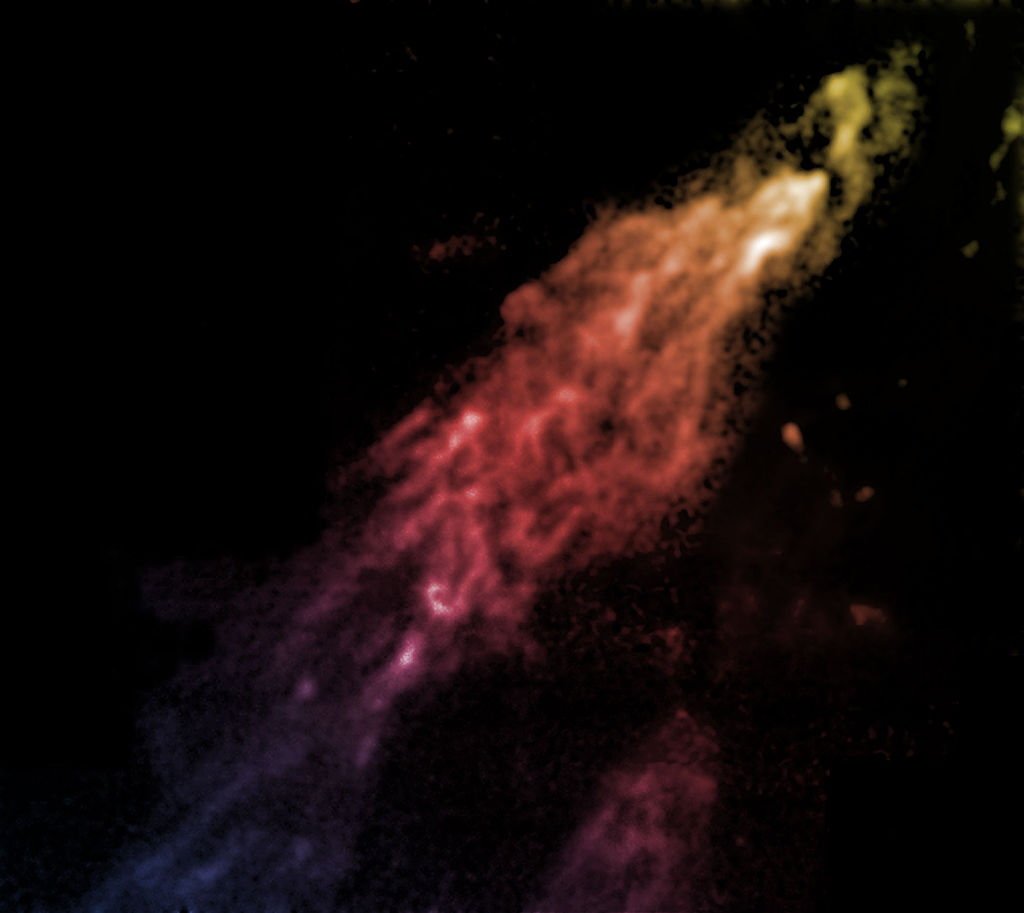

The Smith Cloud
- When was the Smith Cloud discovered?
The cloud (approximately as wide as the Orion constellation) was discovered in 1963 by Gail Bieger, née Smith, who was an astronomy student at Leiden University in the Netherlands.
- Where is the Smith Cloud located?
The phenomenon is 8,000 light years away in the constellation Aquila, located in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for ‘eagle’ and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter’s thunderbolts in Greco-Roman mythology. Aquila lies across the celestial equator.
- What is the Smith Cloud?
The cloud is a high-velocity cloud of hydrogen gas that will have an encounter with the Milky Way Galaxy in 30 million years.
- What will consequences of the impact with the Milky Way be?
When the gigantic Smith Cloud hits, it could set off a tremendous burst of star formation and over a few million years, the impact zone will look like a huge celestial fireworks show, complete with many powerful supernova explosions.
- How fast is the cloud traveling and how would it look like if we could see it?
It is traveling at nearly 700,000 miles per hour and if it were visible to the naked eye, the cloud would have an apparent size of about 20 times the diameter of the moon or it would cover almost as much sky as the constellation Orion.
- Is the Smith Cloud in any way related to the Milky Way?
The cloud appears to have had an intimate relationship with the Milky Way, but was somehow ejected from the outer Milky Way disk about 70 million years ago and is now boomeranging back onto its disk.
- How much hydrogen gas does the Smith Cloud contain?
It contains enough hydrogen to make a million stars like the Sun.
See also:
Gas Cloud Is Speeding Toward Collision With Milky Way – Could The Doom Be Averted?
Smith Cloud Will Crash Into The Milky Way Galaxy In 30 Million Years
Copyright © MessageToEagle.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of MessageToEagle.com
Related Posts
-
 Exomoons May Harbor Extra-Terrestrial Life – Astrophysicist Says
No Comments | Jun 6, 2019
Exomoons May Harbor Extra-Terrestrial Life – Astrophysicist Says
No Comments | Jun 6, 2019 -
 Abell 1758: Rare Collision Of Four Galaxy Clusters Will Form Mega-Structure
No Comments | Dec 8, 2019
Abell 1758: Rare Collision Of Four Galaxy Clusters Will Form Mega-Structure
No Comments | Dec 8, 2019 -
 NASA Cargo Launches To Space Station Aboard Orbital ATK Resupply Mission
No Comments | Dec 7, 2015
NASA Cargo Launches To Space Station Aboard Orbital ATK Resupply Mission
No Comments | Dec 7, 2015 -
 Time Warp And Cloning Of Past Events – How Possible Is It?
No Comments | Dec 19, 2015
Time Warp And Cloning Of Past Events – How Possible Is It?
No Comments | Dec 19, 2015 -
 Discovery Of Extragalactic Neutrino Factories
No Comments | Jul 16, 2022
Discovery Of Extragalactic Neutrino Factories
No Comments | Jul 16, 2022 -
 Seamounts: Gigantic Elevations More Than 1,000 Meters High At The Bottom Of Ocean
No Comments | Mar 26, 2017
Seamounts: Gigantic Elevations More Than 1,000 Meters High At The Bottom Of Ocean
No Comments | Mar 26, 2017 -
 Did Venus Ever Have Oceans? – New Study
No Comments | Oct 14, 2021
Did Venus Ever Have Oceans? – New Study
No Comments | Oct 14, 2021 -
 Solar Orbiter Shows New Detailed Images Of The Full Sun
No Comments | Mar 27, 2022
Solar Orbiter Shows New Detailed Images Of The Full Sun
No Comments | Mar 27, 2022 -
 Ancient Stars’ Orbits Prompt Rethink Theories On Milky Way’s Evolution
No Comments | Nov 19, 2020
Ancient Stars’ Orbits Prompt Rethink Theories On Milky Way’s Evolution
No Comments | Nov 19, 2020 -
 L 98-59b Is The Smallest Planet Yet Discovered By TESS Satellite
No Comments | Jul 1, 2019
L 98-59b Is The Smallest Planet Yet Discovered By TESS Satellite
No Comments | Jul 1, 2019
