Pairs Of Stars Kicked Out Their Host Galaxies Detected By Chandra X-ray Observatory
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – Using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, astronomers discovered that pairs of stars have been kicked out of their host galaxies.
The stellar pairs can consist of combinations of stars like our Sun, or more exotic and denser varieties such as neutron stars or even black holes. Neutron stars form when a massive star explodes as a supernova and the core of the star collapses onto itself. Under certain conditions, these gargantuan blasts that create the neutron star are not symmetric.
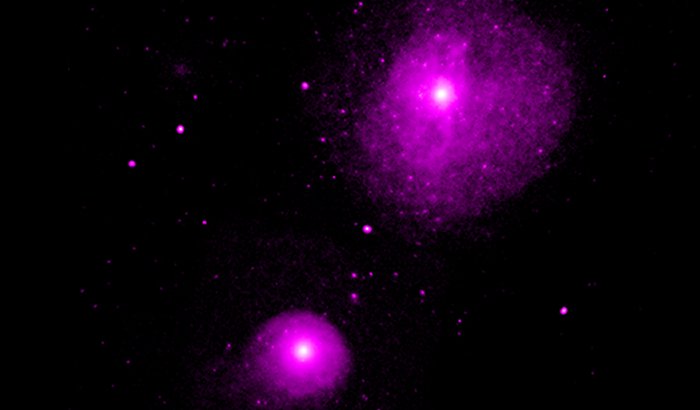 Credit: NASA/CXC/Nanjing University/X. Jin et al.
Credit: NASA/CXC/Nanjing University/X. Jin et al.
The recoil effect can kick the star with such force that it is expelled from the galaxy where it resides.
“It’s like a guest that’s asked to leave a party with a rowdy friend,” Xiangyu Jin of McGill University in Montreal, Canada, who led the study, said in a press release.
“The companion star in this situation is dragged out of the galaxy simply because it’s in orbit with the star that went supernova.”
The team found signatures of so-called X-ray binaries outside of galaxies in a comprehensive study of the Fornax galaxy cluster made with Chandra data taken between 1999 and 2015. This cluster is relatively nearby at a distance of some 60 million light-years from Earth in the constellation sharing its name.
Astronomers concluded that about 30 sources in the Fornax cluster were likely to be pairs of stars that had been kicked out of the center of their host galaxies.
“Rather than being tethered to a particular galaxy, these pairs of stars now exist in the space between galaxies, or are on their way out of their home galaxy,” said co-author Meicun Hou, from Nanjing University in China.
Additionally, another 150 sources that appear to be outside the stellar boundaries of the galaxies within the cluster have also been found.
Based on the Chandra data, astronomers believe there may be many more of these evicted binaries that are too faint to be seen. These populations of fainter sources can be detected with further and longer Chandra observations.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff Writer