MessageToEagle.com – The hottest white dwarf ever discovered in our Galaxy has been identified by astronomers at the Universities of Tübingen and Potsdam, Germany.
With a temperature of 250,000 degrees Celsius, the dying white dwarf, RX J0439.8-6809 located at the outskirts of the Milky Way, has already even entered its cooling phase.
The researchers also were the first to observe an intergalactic gas cloud moving towards the Milky Way – indicating that galaxies collect fresh material from deep space, which they can use to make new stars.
Relatively low-mass stars – like our Sun – get extremely hot towards the end of their lives. The Sun’s surface temperature has been fairly constant at around 6000 degrees Celsius since its birth 4.6 million years ago.

Immediately before its source of nuclear energy is exhausted in about five billion years, the Sun will reach thirty times that temperature, going to 180,000 degrees before cooling down as a white dwarf. Computer simulations suggest that stars can become even hotter than that. The highest temperature of an observed dying star was measured to be 200,000 degrees.
The researchers’ evaluation of ultraviolet spectra taken by the Hubble Space Telescope points to a new record of 250,000 degrees – a temperature which can only be reached by a star some five times more massive than our Sun.
RX J0439.8-6809 appears to have reached its maximum temperature of 400,000 degrees about a thousand years ago. Its chemical composition is not yet understood.
Analyses show that carbon and oxygen are present on its surface – the products of the nuclear fusion of helium, a process which normally takes place deep in the core of a star.
- RX J0439.8-6809 was first noticed more than 20 years ago as a very bright spot on X-ray images, indicating a source of tremendous heat.
- Originally it was thought to be a white dwarf carrying out nuclear fusion on its surface using hydrogen drawn from a companion star.
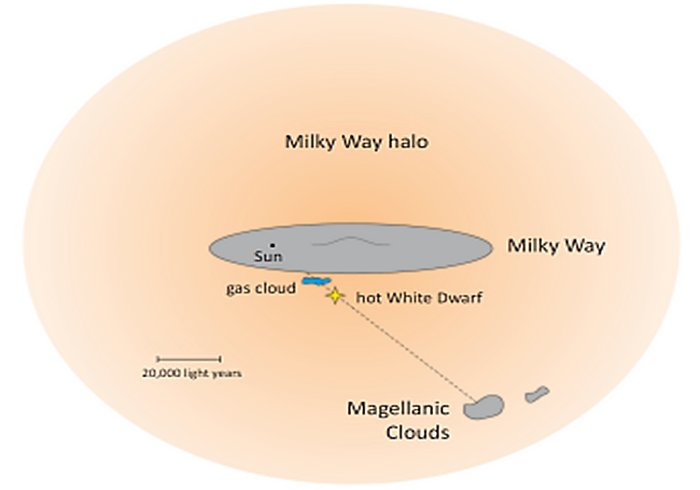
- Astronomers also assumed it was located in our neighboring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud. But the new Hubble data show that the star is on the outskirts of the Milky Way, and is moving away from us at a speed of 220 kilometers per second.
The star’s ultraviolet spectrum held another surprise. It indicates the presence of gas which does not belong to the star; it is part of a cloud between the Milky Way and RX J0439.8-6809. The Doppler effect enables the researchers to determine that this gas cloud is moving away from us at 150 kilometers per second and moves toward the Milky Way. Astronomers knew of the existence of gases traveling at high speed in the direction of the Large Magellanic Cloud, but were unable to tell for sure if they were in the Milky Way or in the LMC.
Finding such gas in the spectrum of RX J0439.8-6809 now offers proof that the gas cloud belongs to the Milky Way. But its chemical composition indicates that it originated from intergalactic space – evidence that galaxies collect fresh material from deep space, which they can use to make new stars.
These findings are published in the latest Astronomy & Astrophysics.
MessageToEagle.com
source: University of Tübingen






