Did Neanderthals And Modern Humans Meet In The Czech Republic 50,000 Years Ago?
MessageToEagle.com – When and where did Neanderthals and modern Humans meet? No-one has been able to answer that question.
Now, a team of archaeologists say there is evidence the transition between Neanderthals and modern humans took place about 50,000 years ago in modern-day Czech Republic.
Artifacts Offer Some Of The Earliest Evidence Of Modern Human Activity In The Region
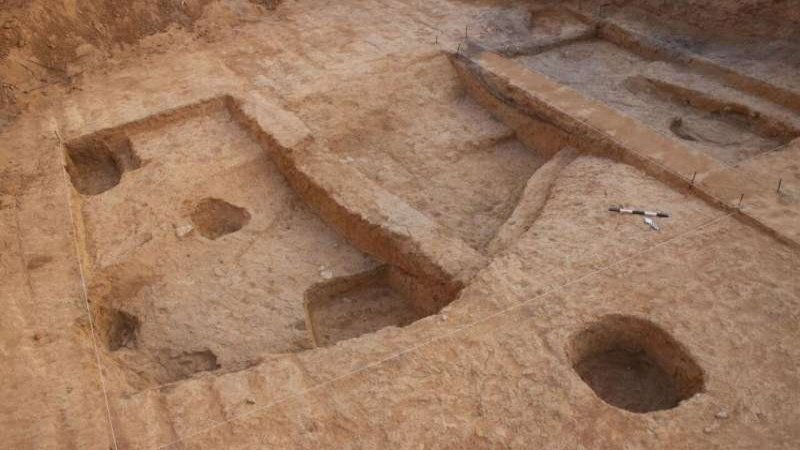
An archaeological dig in a cave in the Moravian region of the Czech Republic has provided a timeline of evidence from 10 sedimentary layers spanning 28,000 to 50,000 years ago. This is the period when our modern human ancestors first arrived in Europe.
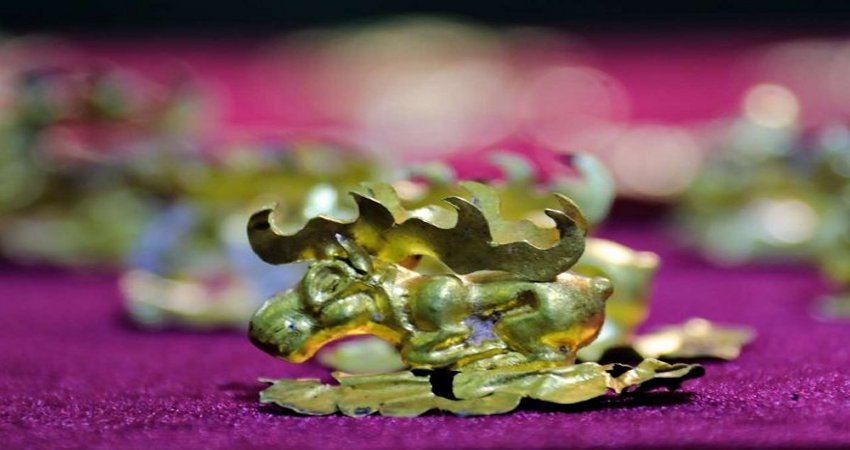
During the excavations archaeologists from the Australian National University (ANU) and the University of Sydney unearthed over 20,000 animal bones as well as stone tools, weapons and an engraved bone bead that is the oldest of its kind in Central Europe.

ANU archaeologist Dr Duncan Wright says the artifacts offer some of the earliest evidence of modern human activity in the region. This was a period when humans were moving substantial distances and bringing with them portable art objects.
“In the early layers the items we’ve found are locally made flakes, possibly used by small communities living and hunting in the vicinity to kill animals or prepare food, but around 40,000 years ago we start to see objects coming from long distances away,” Dr Wright said.
“Dating from this same time we unearthed a bead made from mammal bone. This is the oldest portable art object of its type found anywhere in central Europe and provides evidence of social signalling, quite possibly used as a necklace to mark the identity of the wearer.
“So between these two periods, we’ve either seen a change in behaviour and human movement or possibly even a change in species.”
People Were Very Mobile During This Period
Archaeologist Ladislav Nejman of the University of Sydney explains there is evidence people that somewhere between 40-48,000 years ago people became highly mobile.
“Instead of moving short distances near the cave where they lived, they were walking for hundreds of kilometres quite often. We know that because we found various artefacts where the raw material comes from 100-200 kilometres away.
See also:
10 Surprising Facts About The Neanderthals Who Were Not As Primitive As Previously Thought
Neanderthals Were Present In Italy Much Earlier Than Previously Thought
Toothpicks Were Used Long Before Our Times – Neanderthals Used Them
“The artefacts were also made of different materials from different regions. Some from the North-West, some from the North, some from the East.”
However in layer 10, which represents an earlier time period between 48-45,000 years ago, all the recovered stone artefacts were made using local raw material, which indicates that the high residential mobility came later.
Dr Nejman said the study also revealed valuable new information about the climate of the region.
“We haven’t had such a long sequence of sedimentary layers before that we could test,” he said.

“The climate changed quite often from warmer to colder, and vice versa, but at all times it was much colder than the interglacial period that we have lived in for the past 10,000 years.”
Samples from the site have been sent through for analysis using a new technique, called ancient sediment DNA analysis. This is the first scientific method that can detect which species were present even without the bones of these species. It tests remnant DNA preserved in the sediment.
Dr Wright said the results will shed new light on a period of transition between two species of humans and also give clearer evidence about the activities of our modern human ancestors in a period and region where little is known.
“We can tell by the artefacts that small groups of people camped at this cave. This was during glacial periods suggesting they were well adapted to these harsh conditions” Dr Wright said.
“It’s quite possible that the two different species of humans met in this area.”
MessageToEagle.com
Expand for references