Most Distant Periphery Of The Milky Way – Identified
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – The utmost edge of the Milky Way galaxy has been identified by researchers using the Subaru Telescope’s Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) digital camera .
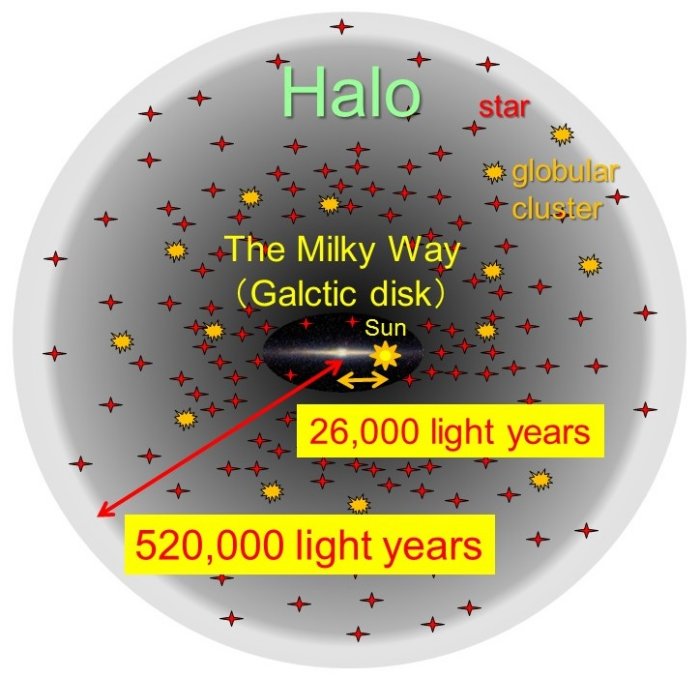
The ultimate size of the galaxy is 520,000 light years in radius, 20 times larger than the distance between the galactic center and our solar system (26,000 light years) (Figure 1).
Stars that reach these outermost regions of the galaxy during their orbital motions are ancient stellar populations with ages as old as 12 billion years.
The spatial extent in which these ancient stars wander is, therefore, important for understanding the Milky Way’s formation.
The galaxy holds a widely extended halo component, in addition to the bright Milky Way in the form of the stellar disk component.
The halo comprises approx. 1 billion ancient stars and 150 globular clusters with ages as old as 12 billion years (Figure 1). The halo thus contains the remnants of long-lived stars and star clusters that formed in the first stage of the galaxy.
This suggests that the galaxy was quite large in its beginning before the later formation of the younger, disk component.
Investigating the expanse of this halo component in the galaxy is comparable to identifying the outer boundary of a forest from inside the forest and observing the trees.
The team of researchers led by Tohoku University graduate student Tetsuya Fukushima and his supervisor Masashi Chiba derived the spatial density of the so-called Blue Horizontal Branch (BHB) stars over the galaxy halo.
While this density generally decreases the further you go from the galactic center, the team discovered a sharp drop in density at around 520,000 light years away from the galactic center.
As a result, the team had finally observed the outermost edge of the galaxy. This is about 20 times larger than the distance between our solar system and the galaxy center.
Our neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy, is reported to have an extended halo component as large as 538,000 (at the very least) light years in radius. It is, therefore, systematically larger when compared to the galaxy halo.
Further mapping of this ancient component of the galaxyis planned.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff
Related Posts
-
 Hubble Shows Winds In Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Are Speeding Up
No Comments | Sep 28, 2021
Hubble Shows Winds In Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Are Speeding Up
No Comments | Sep 28, 2021 -
 Differences Between The Moon’s Near And Far Sides Linked To Colossal Ancient Impact
No Comments | Apr 11, 2022
Differences Between The Moon’s Near And Far Sides Linked To Colossal Ancient Impact
No Comments | Apr 11, 2022 -
 Rare-Earth Metals In Atmosphere Of Hot Exoplanet KELT-9 b – Discovered
No Comments | May 10, 2019
Rare-Earth Metals In Atmosphere Of Hot Exoplanet KELT-9 b – Discovered
No Comments | May 10, 2019 -
 How Quickly The Universe Is Expanding? – New Answers
No Comments | Nov 12, 2019
How Quickly The Universe Is Expanding? – New Answers
No Comments | Nov 12, 2019 -
 UCR Astronomers Have Identified 121 Giant Planets That May Harbor Life
No Comments | May 31, 2018
UCR Astronomers Have Identified 121 Giant Planets That May Harbor Life
No Comments | May 31, 2018 -
 Comet ‘Gateway’ Discovered To Inner Solar System
No Comments | Sep 22, 2019
Comet ‘Gateway’ Discovered To Inner Solar System
No Comments | Sep 22, 2019 -
 Milky Way’s Black Hole Was ‘Birth Cry’ Of Radio Astronomy
No Comments | May 13, 2022
Milky Way’s Black Hole Was ‘Birth Cry’ Of Radio Astronomy
No Comments | May 13, 2022 -
 DTU Scientist Have Confirmed Finding Nearly 100 New Exoplanets
No Comments | Feb 18, 2018
DTU Scientist Have Confirmed Finding Nearly 100 New Exoplanets
No Comments | Feb 18, 2018 -
 Surprisingly High Fraction Of Dead Galaxies Found In Ancient Galactic ‘City’
No Comments | Feb 10, 2022
Surprisingly High Fraction Of Dead Galaxies Found In Ancient Galactic ‘City’
No Comments | Feb 10, 2022 -
 Dyson Spheres: Astronomers Report Potential Candidates For Alien Structures, And Evidence Against Their Existence
No Comments | May 26, 2024
Dyson Spheres: Astronomers Report Potential Candidates For Alien Structures, And Evidence Against Their Existence
No Comments | May 26, 2024