Magma Buildup Discovered Under New Zealand Town
MessageToEagle.com – A magma buildup near the coastal town of Matata in New Zealand, which was discovered, explains a large number of recent earthquakes and could signal the beginnings of a new volcano, researchers say.
However, an eruption is not expected anytime soon.
Geophysicist Ian Hamling said that since 1950, enough magma to fill 80,000 Olympic-size swimming pools has squeezed up beneath the surface near the coastal town of Matata, about 200 kilometers (120 miles) southeast of Auckland.

Hamling, the paper’s lead author, said that while other parts of New Zealand have active volcanoes, there have been none near Matata for at least 400,000 years.
“It was quite a big surprise,” he said in an interview with The Associated Press.
Using GPS data and satellite images, the scientists say they discovered an area of land about 400 square kilometers (154 square miles) has risen by 40 centimeters (16 inches) since 1950.
Hamling said a period of quick uplift between 2004 and 2011 likely triggered thousands of small earthquakes. The magma remained about 10 kilometers (6 miles) below the surface, deep enough that he didn’t expect a volcano to develop within his lifetime. A volcano could develop over hundreds or thousands of years, or the magma could eventually cool and harden, according to Hamling.
Scientists had previously thought tectonic shifts caused the quakes.
Matata is home to about 650 people. Hamling said he hoped further study would allow scientists to develop a warning system for earthquakes in the area. He said the quakes are likely triggered by magma stressing and breaking rock.
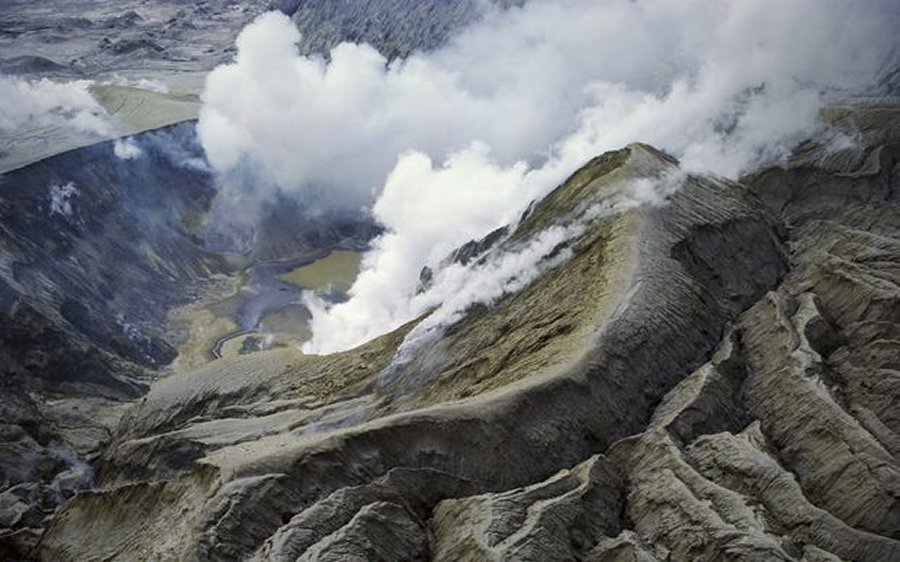
The town is just on the outskirts of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, which is one of the most active volcanic regions in the world.
Hamling said it was unusual worldwide to discover magma buildup in an area with no volcanoes. He said modern equipment allowed them to accurately measure tiny horizontal and vertical changes in the coastal land.
Just over half of the area studied is offshore, however, and Hamling said the scientists needed to rely on inferences from what happened on the land to gauge the changes underwater.
“The scientific analysis seems robust and notes the limitations of modelling an offshore source,” according to Victoria Miller, a volcanologist with Geoscience Australia who was not involved in the research.
Miller said the location was of interest because it was outside of an active volcanic area.
A paper on the subject was published Saturday in the online journal Science Advances.
MessageToEagle.com
Expand for references