First Probable Impact Crater – Buried At A Depth Of 1,000 M – Identified In Spain
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – The first probable impact crater in Spain has been identified in the southern province of Almeria.
The discovery was presented last week at the Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC) 2022 by Juan Antonio Sánchez Garrido of the University of Almeria.
Location of the crater center and 20-kilometer radius of the area affected by the impact in the Alhabia-Tabernas basin. Credit: Sánchez-Garrido et al.
While around 200 impact structures have been identified around the world, the study is the first to identify signs of an impact crater on the Iberian Peninsula.
The discovery is the result of 15 years of research by an international team of scientists from the University of Almeria, the Astrobiology Center of Madrid, the University of Lund and the University of Copenhagen.
Prof Sánchez Garrido says, “We believe that the impact event occurred around 8 million years ago. We have investigated numerous aspects of the geology, minerology, geochemistry and geomorphology of the region.
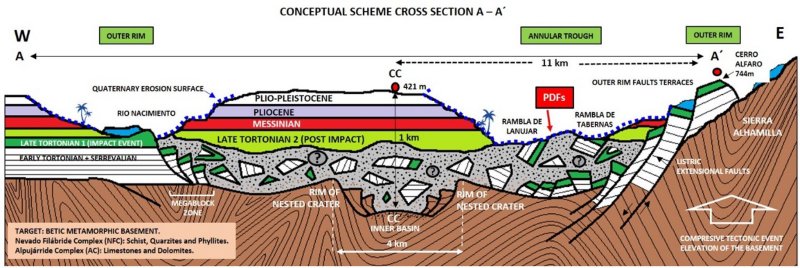
Much of the impact structure is buried by the most recent sediments. The crater itself is 4 kilometers in diameter and is buried at a depth of 1000 m. The edge of the structure reaches a diameter of 20 kilometers. Credit: Sánchez-Garrido et al 2022.
The basins of Alhabia and Tabernas in the area are filled with sediments dating back between 5 and 23 million years, and they overlie older metamorphic rocks. Much of the impact structure is buried by more modern sediments, but erosion has exposed it and opened up the opportunity for studies.”
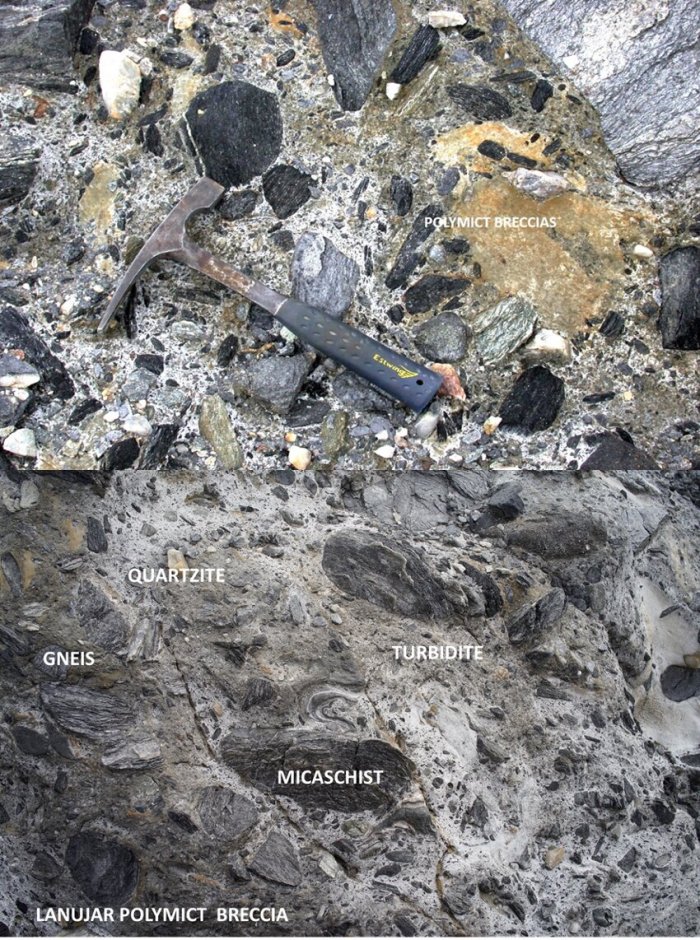
Evidence for the impact crater includes several examples of ‘shocked’ quartz grains in breccia – a sedimentary rock type with large fragments cemented into a finer-grained matrix. The grains show signs of being deformed in the enormous pressures of the impact, which were between 10 and 30 gigapascals. Credit: Sánchez-Garrido et al 2022.
The crater itself is thought to be about 4 kilometers in diameter, and it is surrounded by a larger structure about 20 kilometers across where the impact caused the sedimentary strata to collapse.
Thin sections showing deformations in three quartz grains, produced by shock effects, in an impact breccia at Tabernas. Credit: Sánchez-Garrido et al 2022.
Evidence for the impact crater includes several examples of “shocked” quartz grains in breccia—a sedimentary rock type with large fragments cemented into a finer-grained matrix. The grains show signs of being deformed in the enormous pressures of the impact, which were between 10 and 30 gigapascals.
“If the crater discovery is confirmed, it would not only be exciting from a scientific perspective, but would also be a wonderful addition to the scientific and touristic attractions of the province of Almeria,” said Prof Sánchez Garrido, in a press release.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff Writer