Earth’s Atmosphere Stretches Almost Twice The Distance To the Moon And Beyond
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – Earth’s atmosphere extends well beyond the lunar orbit – almost twice the distance to the Moon.
The outermost part of our planet’s atmosphere extends well beyond the lunar orbit – almost twice the distance to the Moon, according to a new research based on observations by the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, SOHO.
The results show that the gaseous layer that wraps around Earth reaches up to 630 000 km away, or 50 times the diameter of our planet.
“The Moon flies through Earth’s atmosphere,” says Igor Baliukin of Russia’s Space Research Institute, lead author of the paper.
“We were not aware of it until we dusted off observations made over two decades ago by the SOHO spacecraft.”
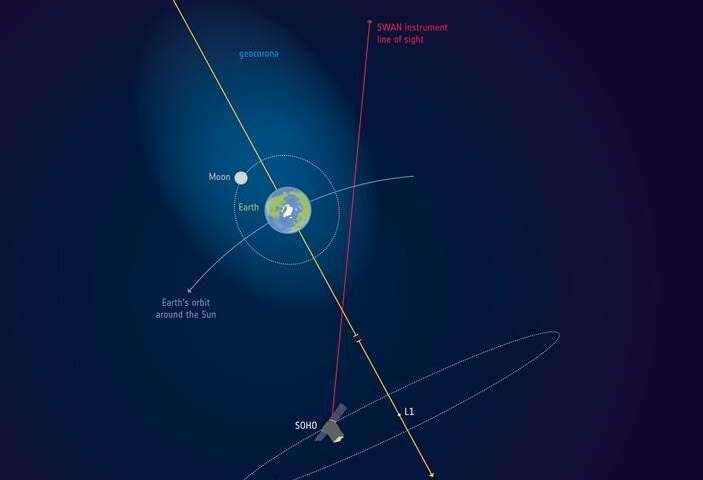
Where our atmosphere merges into outer space, there is a cloud of hydrogen atoms called the geocorona. One of the spacecraft instruments, SWAN, used its sensitive sensors to trace the hydrogen signature and precisely detect how far the very outskirts of the geocorona are.
These observations could be done only at certain times of the year, when the Earth and its geocorona came into view for SWAN.
For planets with hydrogen in their exospheres, water vapor is often seen closer to their surface. That is the case for Earth, Mars and Venus.
“This is especially interesting when looking for planets with potential reservoirs of water beyond our Solar System,” explains Jean-Loup Bertaux, co-author and former principal investigator of SWAN.
The first telescope on the Moon, placed by Apollo 16 astronauts in 1972, captured an evocative image of the geocorona surrounding Earth and glowing brightly in ultraviolet light.
“At that time, the astronauts on the lunar surface did not know that they were actually embedded in the outskirts of the geocorona,” says Jean-Loup.
Launched in December 1995, the SOHO space observatory has been studying the Sun, from its deep core to the outer corona and the solar wind, for over two decades. The satellite orbits around the first Lagrange point (L1), some 1.5 million kilometres from Earth towards the Sun.
The Sun interacts with hydrogen atoms through a particular wavelength of ultraviolet light called Lyman-alpha, which the atoms can both absorb and emit. Since this type of light is absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere, it can only be observed from space.
Thanks to its hydrogen absorption cell, the SWAN instrument could selectively measure the Lyman-alpha light from the geocorona and discard hydrogen atoms further out in interplanetary space.
The new study revealed that sunlight compresses hydrogen atoms in the geocorona on Earth’s dayside, and also produces a region of enhanced density on the night side. The denser dayside region of hydrogen is still rather sparse, with just 70 atoms per cubic centimeter at 60 000 kilometers above Earth’s surface, and about 0.2 atoms at the Moon’s distance.
“On Earth we would call it vacuum, so this extra source of hydrogen is not significant enough to facilitate space exploration,” says Igor.
“There is also ultraviolet radiation associated to the geocorona, as the hydrogen atoms scatter sunlight in all directions, but the impact on astronauts in lunar orbit would be negligible compared to the main source of radiation – the Sun,” says Jean-Loup Bertaux.
On the down side, the Earth’s geocorona could interfere with future astronomical observations performed in the vicinity of the Moon.
“Space telescopes observing the sky in ultraviolet wavelengths to study the chemical composition of stars and galaxies would need to take this into account,” adds Jean-Loup.
SOHO’s SWAN instrument imaged Earth and its extended atmosphere on three occasions between 1996 and 1998.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff Writer