Conny Waters – MessageToEagle.com – Researchers have analyzed the genome of the oldest human fossil found in Mongolia to date and show that the 34,000-year-old woman inherited around 25 percent of her DNA from western Eurasians.

The skullcap found in the Salkhit Valley in eastern Mongolia belonged to a woman who lived 34,000 years ago. Analyses showed: She had inherited about 25 percent of her DNA from Western Eurasian. Credit: Institute of Archaeology, Mongolian Academy of Sciences
The result shows that people moved across the Eurasian continent shortly after it had first been settled by the ancestors of present-day populations. This individual and a 40,000-year-old individual from China also carried DNA from Denisovans, an extinct form of hominins that inhabited Asia before modern humans arrived.
It is known that Denisovans occupied the Tibetan Plateau in the Middle Pleistocene and successfully adapted to high-altitude and the region’s harsh climate.
Denisovans, an extinct sister group of Neandertals, were discovered in 2010, and then, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (MPI-EVA) sequenced the genome of a fossil finger bone found at Denisova Cave in Russia and showed that it belonged to a hominin group that was genetically distinct from Neandertals.
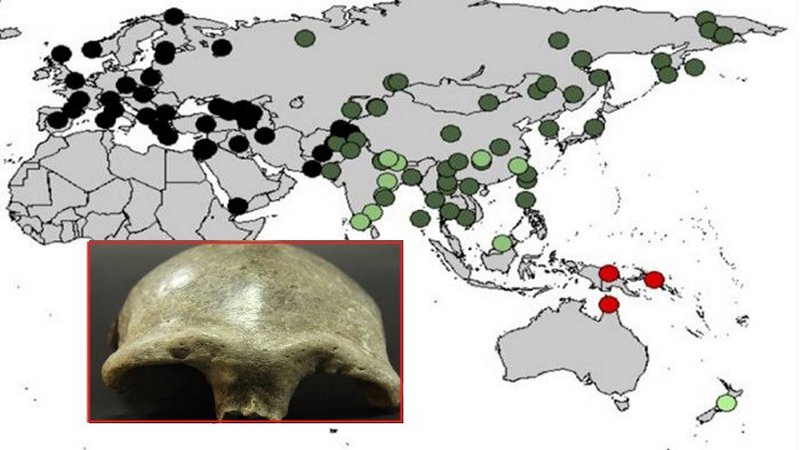
According to researchers, these ancient hominins may have once been widespread because their DNA traces have been found in present-day Asian, Australian, and Melanesian populations.

The Salkhit Valley, Mongolia © Institute of History and Archaeology & Academy of Sciences (Mongolia).
In 2006, miners discovered a hominin skullcap with peculiar morphological features in the Salkhit Valley of the Norovlin county in eastern Mongolia. The skullcap is considered the only Pleistocene hominin fossil found in Mongolia.
Initially, it was referred to as Mongolanthropus and thought to be a Neandertal or even a Homo erectus. The remains of the “Salkhit” individual represent the only Pleistocene hominin fossil found in the country.
Ancient DNA extracted from the skullcap shows that it belonged to a female modern human who lived 34,000 ago and was more related to Asians than to Europeans.
Comparisons to the only other early East Asian individual genetically studied to date, a 40,000-year-old male from Tianyuan Cave outside Beijing (China), show that the two individuals are related to each other. However, they differ insofar that a quarter of the ancestry of the Salkhit individual derived from western Eurasians, probably via admixture with ancient Siberians.
In humans today, concentrations of Denisovan DNA is highest in Australia and Papua New Guinea (red), but the new study found higher-than-expected levels in South Asia (light green). UCLA/Harvard Medical School
“This is direct evidence that modern human communities in East Asia were already quite cosmopolitan earlier than 34,000 years ago,” says Diyendo Massilani, lead author of the study and researcher at the Max-Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
“This rare specimen shows that migration and interactions among populations across Eurasia happened frequently already some 35,000 years ago.”
The researchers at the Max-Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology used a new method to find segments of DNA from extinct hominins in the Salkhit and Tianyuan genomes.
See also:
Denisovan Family Tree: New Branches Revealed In Ancient DNA
Enigmatic Denisovans Interbred With Modern Humans More Than Once
Mysterious Ancient Human ‘Ghost’ Species Discovered With Help Of Saliva
Denisovan DNA Detected In Modern South Asians – UCLA Scientists Reveal
Mysterious Archaic Cavemen – Denisovans – Were Relatives To Neanderthals And Humans
They found that the two genomes contain not only Neandertal DNA but also DNA from Denisovans, an elusive Asian relative of Neandertals.
“It is fascinating to see that the ancestors of the oldest humans in East Asia from whom we have been able to obtain genetic data had already mixed with Denisovans, an extinct form of hominins that has contributed ancestry to present-day populations in Asia and Oceania,” says Byambaa Gunchinsuren, a researcher at the Institute of Archaeology of the Mongolian Academy of Sciences.
“This is direct evidence that Denisovans and modern humans had met and mixed more than 40,000 years ago.”
“Interestingly, the Denisovan DNA fragments in these very old East Asians overlap with Denisovan DNA fragments in the genomes of present-day populations in East Asia but not with Denisovan DNA fragments in Oceanians. This supports a model of multiple independent mixture events between Denisovans and modern humans,” says Massilani.
Written by Conny Waters – MessageToEagle.com – AncientPages.com Staff Writer