Changes In Jupiter’s Magnetic Field Found By Juno Mission
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – NASA’s Juno mission to Jupiter made the first definitive detection beyond our world of an internal magnetic field that changes over time, a phenomenon called secular variation.
Juno determined the gas giant’s secular variation is most likely driven by the planet’s deep atmospheric winds.
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot and turbulent southern hemisphere was captured by NASA’s Juno spacecraft as it performed a close pass of the gas giant planet. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill
“Secular variation has been on the wish list of planetary scientists for decades,” Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, said in a press release.
This discovery could only take place due to Juno’s extremely accurate science instruments and the unique nature of Juno’s orbit, which carries it low over the planet as it travels from pole to pole.”
Compared data from NASA’s past missions to Jupiter (Pioneer 10 and 11, Voyager 1 and Ulysses) to a new model of Jupiter’s magnetic field (called JRM09), showed that from the first Jupiter magnetic field data provided by the Pioneer spacecraft through to the latest data provided by Juno, there were small but distinct changes to the field.
“Finding something as minute as these changes in something so immense as Jupiter’s magnetic field was a challenge,” said Kimee Moore, a Juno scientist from Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
“Having a baseline of close-up observations over four decades provided us with just enough data to confirm that Jupiter’s magnetic field does indeed change over time.”
Once the Juno team proved secular variation did occur, they sought to explain how such a change might come about. The operation of Jupiter’s atmospheric (or zonal) winds best explained the changes in its magnetic field. These winds extend from the planet’s surface to over 1,860 miles (3,000 kilometers) deep, where the planet’s interior begins changing from gas to highly conductive liquid metal. They are believed to shear the magnetic fields, stretching them and carrying them around the planet.
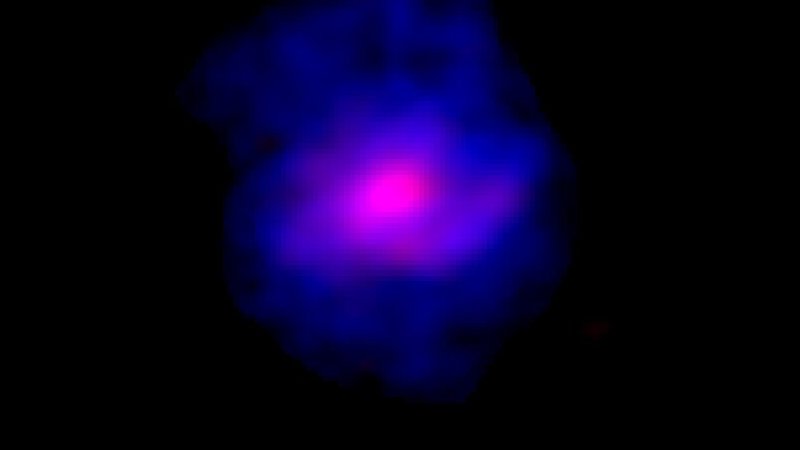
Nowhere was Jupiter’s secular variation as large as at the planet’s Great Blue Spot, an intense patch of magnetic field near Jupiter’s equator. The combination of the Great Blue Spot, with its strong localized magnetic fields, and strong zonal winds at this latitude result in the largest secular variations in the field on the Jovian world.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff Writer