Astronomers And ALMA Spot Monstrous Baby Galaxies 11.5 Billion Light-Years Away
MessageToEagle.com – Using the ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array), astronomers discovered a nest of monstrous baby galaxies located 11.5 billion light-years away.
The young galaxies seem to reside at the junction of gigantic filaments in a web of dark matter.
These findings are important for understanding how monstrous galaxies like these are formed and how they evolve in to huge elliptical galaxies.
Ten billion years ago, long before the Sun and Earth were formed, areas of the Universe were inhabited by monstrous galaxies with star formation rates hundreds or thousands of times what we observe today in the Milky Way galaxy.
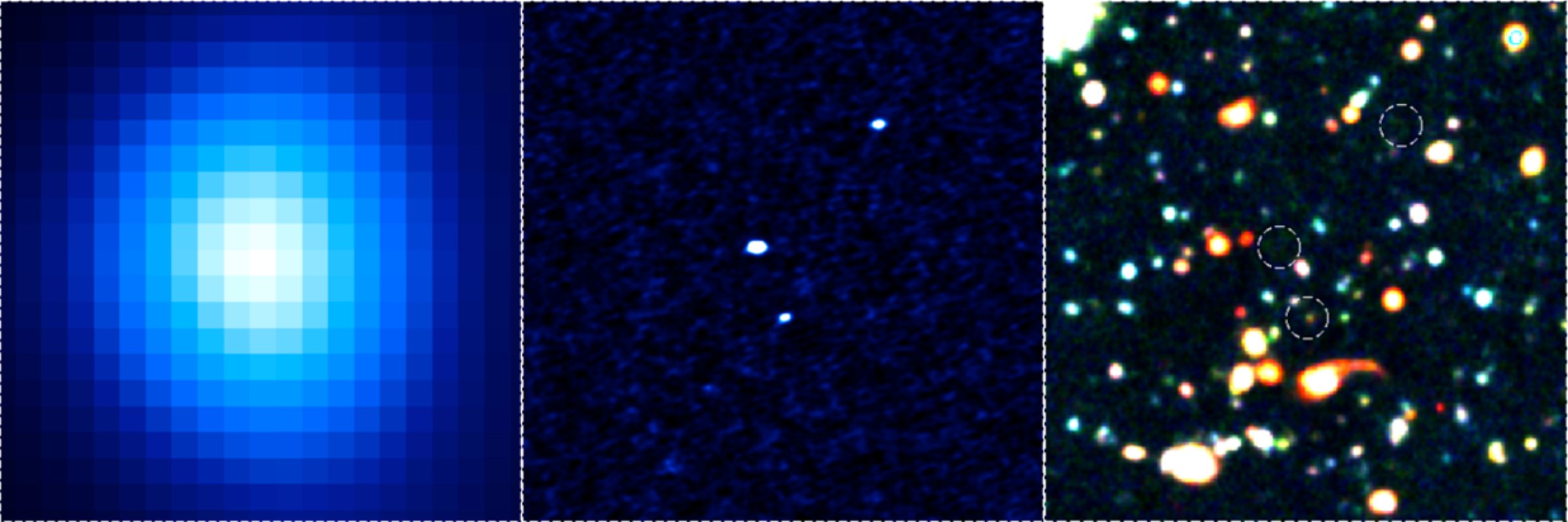
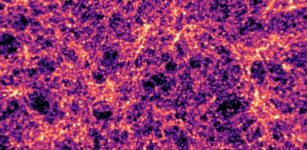
Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), NAOJ, H. Umehata (The University of Tokyo)
There aren’t any monstrous galaxies left in the modern Universe, but astronomers believe that these young galaxies matured into giant elliptical galaxies which are seen in the modern Universe.
However, until now, it has been difficult to determine the positions of active star forming galaxies because they are often obscured in dust, making them difficult to observe in visible light. Dusty galaxies do emit strong radio waves with submillimeter wavelengths, but radio telescopes typically have not had the resolution needed to pin-point individual galaxies.
To search for monstrous galaxies, astronomers used ALMA to make extensive observations of a small part of the sky called SSA22 in the constellation Aquarius (the Water-Bearer).
With ten times better sensitivity and 60 times better resolution, ALMA enabled astronomers to pinpoint the locations of nine monstrous galaxies in SSA22.
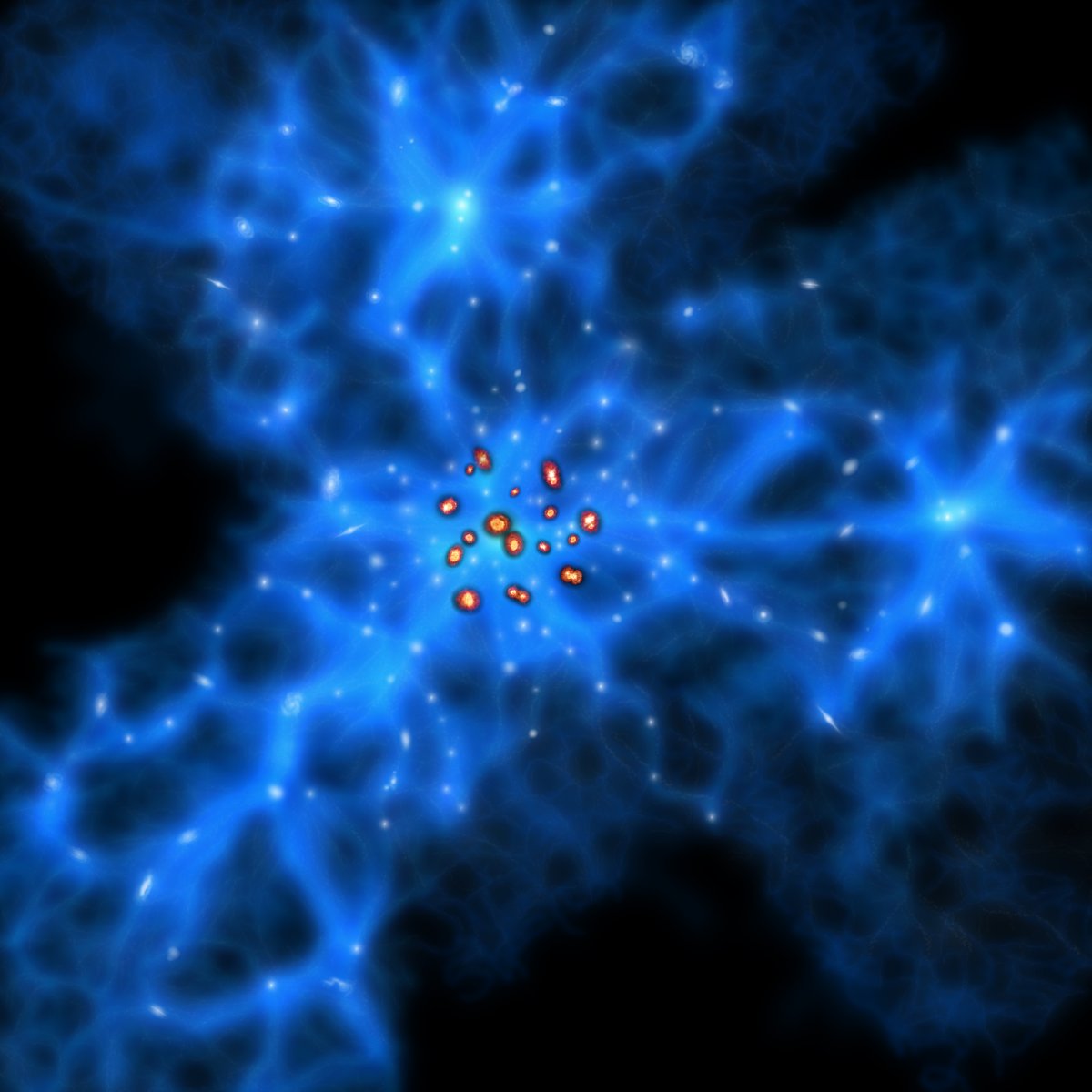
The team compared the positions of these galaxies with the location of a cluster of young galaxies 11.5 billion light-years from Earth in SSA22 which had been studied in visible light by the Subaru Telescope, operated by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ).
The shape of the cluster observed by the Subaru Telescope indicates the presence of a huge 3D web of invisible dark matter.
This dark matter filamentary structure is thought to be a progenitor of large scale structures in the Universe.

(One of the best known examples of large scale structure in the modern Universe is the cosmic Great Wall, a gigantic filamentary structure spanning over 500 million light-years.)
The filamentary structure in SSA22 could be called a proto-Great Wall.
The team found that their young monstrous galaxies seemed to be located right at the intersection of the dark matter filaments.
This finding supports the model that monstrous galaxies form in areas where dark matter is concentrated.
This result is a very important step for a comprehensive understanding of the relation between the dark matter distribution and monstrous galaxies.
Research paper – arXiv
MessageToEagle.com