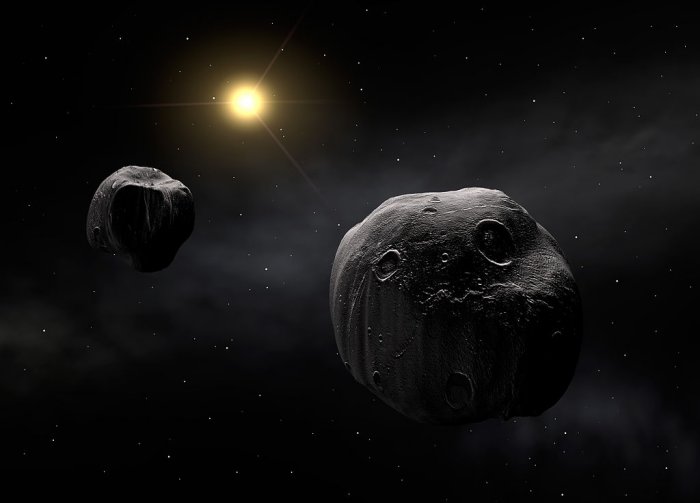
Asteroids Have Days And Nights But The Yarkovsky Effect Is Dangerous
A. Sutherland – MessageToEagle.com – Just like planets and moons, asteroids orbit the Sun and they have days and nights. During its orbit around the Sun, every part of the asteroid’s surface sees sunlight, but that is not always a good thing.
Earth’s rotation period is about 24 hours, but some asteroids are faster or slower. An asteroid’s rotation rates depend on both asteroidal type and diameter and direction of rotation can differ for each individual asteroid. Asteroid 2008 HJ is very small, only 12 meters by 24 meters (39.4 feet by 78.7 feet) and it completes a rotation every 42.7 seconds. This is fastest asteroid rotation observed by astronomers.
Other asteroids take more time to complete an orbit around the Sun, usually between one hour and 80 hours.
See also:
What Is The Color Of The Sky On An Exoplanet?
Forbush Decrease: Dangerous Event That Can Affect Human Health, Technology, Earth’s Environment
Phenomenon Of True Polar Wander: What Is It?
An asteroid has an average orbital speed (how fast an object orbits the Sun) of 25 kilometers per second. However, asteroids orbiting closer to a Sun will move faster than asteroids orbiting between Mars and Jupiter and beyond. It’s also important to remember that passing by the gravitational fields of planets, such as Earth, can change the rotation or spin of asteroids.
Why Is The Yarkovsky Effect Dangerous?
Until now, there are no records of any asteroid that has hit the Sun, but it doesn’t mean it’s an impossible scenario. However, sunlight has the ability to change the course of asteroids and drastically alter the layout of the solar system. Rotating asteroids have a tough time sticking to their orbits.
When sunlight strikes a rotating asteroid, the dayside heats up; as the asteroid turns, the night side cools and releases the heat, exerting a small thrust that can change the asteroid’s direction over time.
This force, called the Yarkovsky effect, can cause rotating asteroids to drift widely over time, making it hard for scientists to predict their long-term risk to Earth.
Written by – A. Sutherland – MessageToEagle.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © MessageToEagle.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of MessageToEagle.com
Related Posts
-
 Could A Twin Earth Detect Earth? What Does Earth Look Like To The Rest Of The Galaxy?
No Comments | Feb 4, 2025
Could A Twin Earth Detect Earth? What Does Earth Look Like To The Rest Of The Galaxy?
No Comments | Feb 4, 2025 -
 Black Hole Eruption Spanning 16 Times The Full Moon In The Sky – Captured
No Comments | Dec 23, 2021
Black Hole Eruption Spanning 16 Times The Full Moon In The Sky – Captured
No Comments | Dec 23, 2021 -
 New Monster Black Hole ‘Practically In Our Back Yard’ – Discovered
No Comments | Oct 20, 2022
New Monster Black Hole ‘Practically In Our Back Yard’ – Discovered
No Comments | Oct 20, 2022 -
 Gravitational Self-Lensing Of Massive Black Hole Binaries
No Comments | Oct 22, 2021
Gravitational Self-Lensing Of Massive Black Hole Binaries
No Comments | Oct 22, 2021 -
 Milky Way’s Supermassive Black Hole May Have ‘Unseen’ Siblings
No Comments | Apr 25, 2018
Milky Way’s Supermassive Black Hole May Have ‘Unseen’ Siblings
No Comments | Apr 25, 2018 -
 Active Galactic Nuclei Are Even More Powerful Than Thought – New Study
No Comments | Jan 16, 2023
Active Galactic Nuclei Are Even More Powerful Than Thought – New Study
No Comments | Jan 16, 2023 -
 Ancient Bacteria Might Lurk Beneath Mars’ Surface
No Comments | Oct 26, 2022
Ancient Bacteria Might Lurk Beneath Mars’ Surface
No Comments | Oct 26, 2022 -
 First Underground Radar Images From Mars Perseverance Rover Reveal Some Surprises
No Comments | Aug 27, 2022
First Underground Radar Images From Mars Perseverance Rover Reveal Some Surprises
No Comments | Aug 27, 2022 -
 Largest Flare Ever Recorded From Proxima Centauri, The Sun’s Nearest Neighbor Observed By Astronomers
No Comments | Apr 23, 2021
Largest Flare Ever Recorded From Proxima Centauri, The Sun’s Nearest Neighbor Observed By Astronomers
No Comments | Apr 23, 2021 -
 Nampa Figurine That Strongly Challenges The Evolutionary Scenario: Controversial Case Of Extreme Human Antiquity
No Comments | May 11, 2014
Nampa Figurine That Strongly Challenges The Evolutionary Scenario: Controversial Case Of Extreme Human Antiquity
No Comments | May 11, 2014

