ALMA’s Observations Of Protostar G353 In Constellation Scorpius
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – Astronomers used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to observe a massive protostar called G353.273+0.641 (hereafter G353).
They obtained the first detailed face-on view of a gaseous disk feeding the growth of a massive baby star. The process shares many common features with lighter baby stars. This implies that the process of star formation is the same, regardless of the final mass of the resulting star.
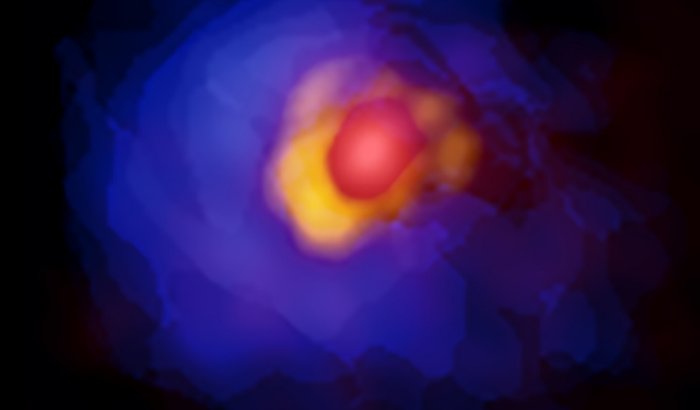 ALMA image of the massive protostar G353.273+0.641. Comact emission around the central protostar, disk, and gaseous envelope are shown in red, yellow, and blue. Asymmetry in the disk is clearly shown with the high resolution ALMA observations. Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), Motogi et al.
ALMA image of the massive protostar G353.273+0.641. Comact emission around the central protostar, disk, and gaseous envelope are shown in red, yellow, and blue. Asymmetry in the disk is clearly shown with the high resolution ALMA observations. Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), Motogi et al.
A protostar, a baby star still in the process of forming, is fed by a surrounding disk of gas falling towards the center. It is located 5500 light-years away in the constellation Scorpius, G353 has a mass 10 times larger than the Sun, and is still growing. It is a unique target among massive protostars because we can see its gaseous disk from straight above. ALMA has revealed detailed views of several other massive infant stars, however, most of them are in edge-on configurations, making it difficult to see the inner regions of the disks.
ALMA observations captured a rotating disk around G353 with a radius eight times larger than the orbit of Neptune. This sounds huge, but it is one of the smallest disks yet found around a massive protostar. ALMA also found that the disk is surrounded by an envelope of gas three times larger than the disk.
 Artist’s impression of the gaseous disk and envelope around the massive protostar G353.273+0.641.Credit: National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
Artist’s impression of the gaseous disk and envelope around the massive protostar G353.273+0.641.Credit: National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
“We measured the gas infall rate from the outer envelope to the inner disk,” Kazuhito Motogi, an assistant professor at Yamaguchi University, Japan, who led his team in this study, said in a press release.
“This helps us to estimate the age of the baby star. Surprisingly it is only 3000 years old, the youngest among known massive protostars. We are witnessing the earliest phase of the growth of a giant star.”
Interestingly, the disk is not uniform; the south-eastern side of the disk is brighter than other parts. This is the first time astronomers have seen an asymmetric disk around a massive protostar. The team also found that the disk is highly unstable and going to fragment.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff